COPD (Chronic Obstruction Pulmonary Disease) ?
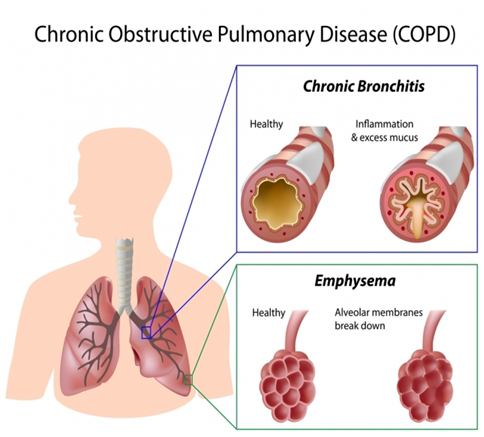
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD, refers to a group of diseases that cause airflow blockage and breathing-related problems. It includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis. COPD makes breathing difficult for millions of people who suffer from this disease. Millions more people suffer from COPD, but have not been diagnosed and are not being treated.
Could you have COPD?
The main cause of COPD is tobacco smoke, so if you smoke or used to smoke, you are at a higher risk of having COPD. Exposure to air pollution in the home or at work, family history, and respiratory infections like pneumonia, also increase your risk.
How is COPD diagnosed;
COPD is diagnosed using a simple breathing test called spirometry.
How is COPD treated?
Treating your COPD can greatly improve your quality of life. Treatment options that your doctor may consider include:
Stop smoking. For people who smoke, the most important aspect of treatment is to stop smoking.
Avoid tobacco smoke and other air pollutants at home and at work.
Medication. Symptoms such as coughing or wheezing can be treated with inhaler medications.
Pulmonary rehabilitation, a personalized treatment program that teaches you how to manage your COPD symptoms to improve quality of life. Plans may include learning to breathe better, how to conserve your energy, and advice on food and exercise.
Avoid lung infections. Lung infections can cause serious problems in people with COPD. Certain vaccines, such as flu and pneumonia vaccines, are especially important for people with COPD. Respiratory infections should be treated with antibiotics, if appropriate.
Supplemental oxygen from a portable oxygen tank may be needed if blood oxygen levels are low.